Key 5G capabilities
Industrial 5G Usage
One of the main differences between 5G and previous generations of cellular networks lies in 5G’s strong focus on machine-type communication and the Internet of Things (IoT). The capabilities of 5G thus extend far beyond mobile broadband with ever increasing data rates.
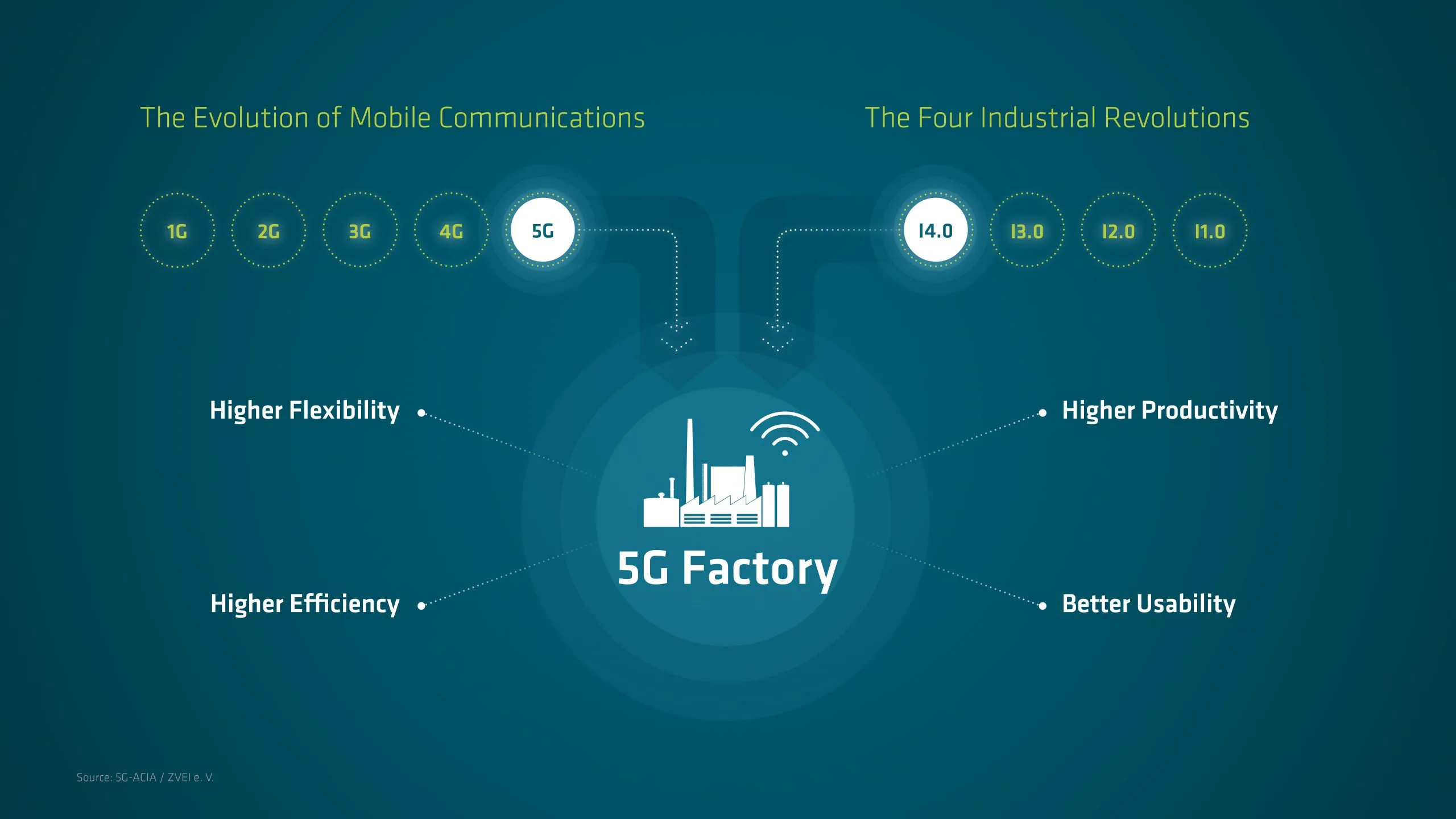
Key 5G capabilities pave the way for perfecting Industry 4.0
In particular, 5G supports communication with unprecedented reliability and very low latencies, as well as massive IoT connectivity. This paves the way for the next era in industrial production, known as “Industry 4.0”, which aims to significantly improve the flexibility, versatility, usability and efficiency of future smart factories and industrial plants. Industry 4.0 integrates the IoT and related services in industrial manufacturing, and delivers seamless vertical and horizontal integration down the entire value chain and across all layers of the automation pyramid. Connectivity is a key component of Industry 4.0 and will support the ongoing developments by providing powerful and pervasive connectivity between machines, people and objects.
Key Enabler
Key 5G features for a new industrial revolution
The rationale for the development of the 5th generation of mobile communications (5G) was not only to expand the broadband capabilities of mobile networks, but also to provide advanced wireless connectivity for a wide variety of vertical industries, such as the manufacturing, automotive and agricultural sectors. To achieve this, 5G supports three essential types of communication: enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB), massive machine-type communication (mMTC), and ultra-reliable low-latency communications (URLLC).
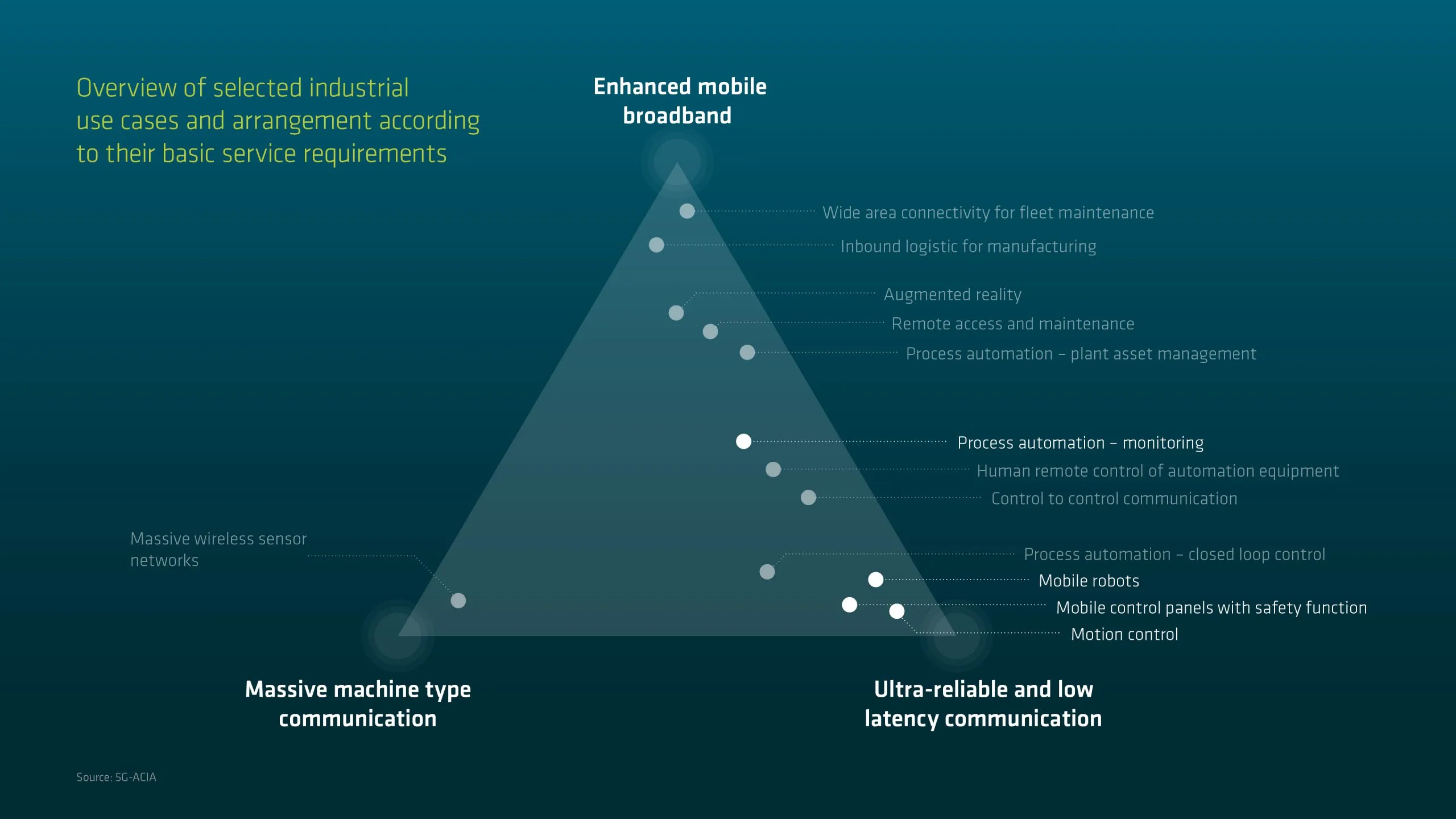
Overview of selected industrial use cases
eMBB provides extremely high data rates (of up to several Gb/s) and offers enhanced coverage, well beyond that of 4G. mMTC is designed to provide wide-area coverage and deep indoor penetration for hundreds of thousands of IoT devices per square kilometer. In addition, mMTC is designed to provide ubiquitous connectivity with low software and hardware requirements from the devices, and will support battery-saving low-energy operation. URLLC can facilitate highly critical applications with very demanding requirements in terms of end-to-end (E2E) latency (down to the millisecond level), reliability and availability.This includes, for example, high-performance connectivity for applications in industrial automation and control. Some of the target key performance indicators of 5G as specified by the International Telecommunications Union (ITU) are summarized below. In order to support the three service types defined above and the diverse requirements of the anticipated 5G use cases by a common cellular infrastructure, network slicing, a new concept introduced in 5G, will allow simultaneous but isolated provisioning of diverse services by the same network infrastructure.
Key performance indicators
- High data rates
- Low latency
- Long battery lifetime
- Ultra-reliable
- Security-by-design
- High positioning accuracy
- High availability
- TSN support
- High synchronicity
- Deterministic communication
- Real-time support
- High connection density
- Dependable communication
- Non-public networks
- Network slicing