Deterministic Networking (DetNet) is an outcome of efforts by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) DetNet Working Group to develop a new layer 3 technology with time-sensitive features. It is relevant to industrial automation use cases for the fifth generation of wireless cellular technology (5G).
This white paper reviews the architecture and features of DetNet and how it relates to IEEE 802.1 Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN). It discusses the technology’s applicability to and potential benefits for a variety of 5G industrial use cases and scenarios, including interconnection of TSN segments and cases in which controllers are located in an on-premises edge cloud. Interconnections in which DetNet provides layer-3 connectivity with time-sensitive features may be a powerful solution for some 5G industrial use cases.
Also covered are the current status and limitations of ongoing standardization efforts. The IETF DetNet Working Group has already made substantial progress, but some aspects — including the DetNet controller plane — are still being debated. 3GPP Release 18 already provides standardized 5G support for DetNet under some architectural assumptions.
Key insights are derived by looking at DetNet’s most useful features, how it relates to TSN, the support that 3GPP provides for it in the form of logical DetNet nodes in 5G, its relevance to 5G industrial use cases, and how it could be used in typical manufacturing network situations.
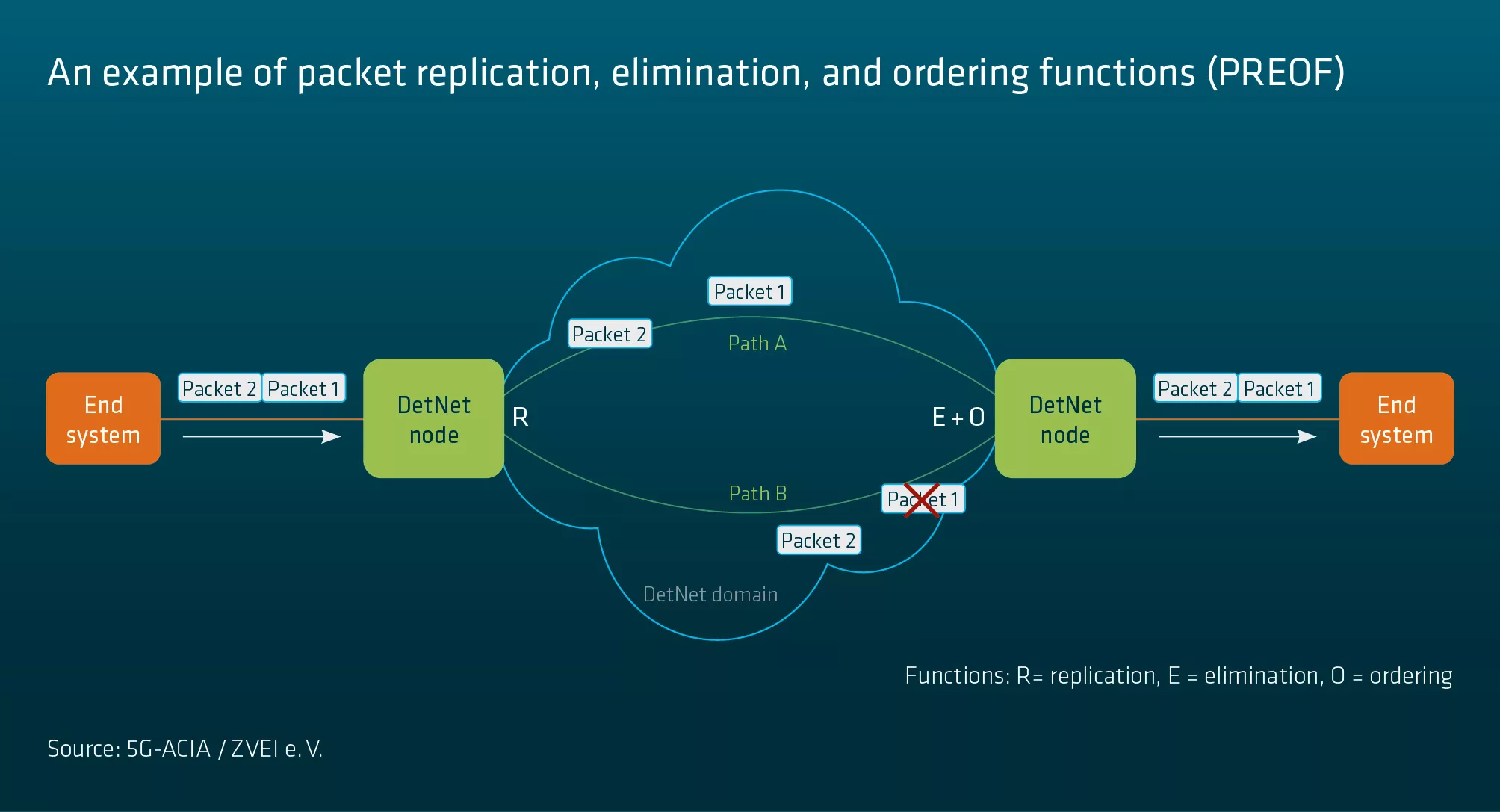
DetNet includes a feature set that is able to deliver the promised benefits: very low delay, extremely low packet loss, and in-order packet delivery. To minimize delays, resources (such as bandwidth and buffer space) are allocated to devices within the DetNet domain. The use of explicit routes protects services and controls congestion while providing immunity against IP protocol convergence caused by changes in topology. Redundant paths with packet replication and elimination functions minimize packet losses. Finally, use of a packet ordering function can also ensure in-order packet delivery with redundant paths.
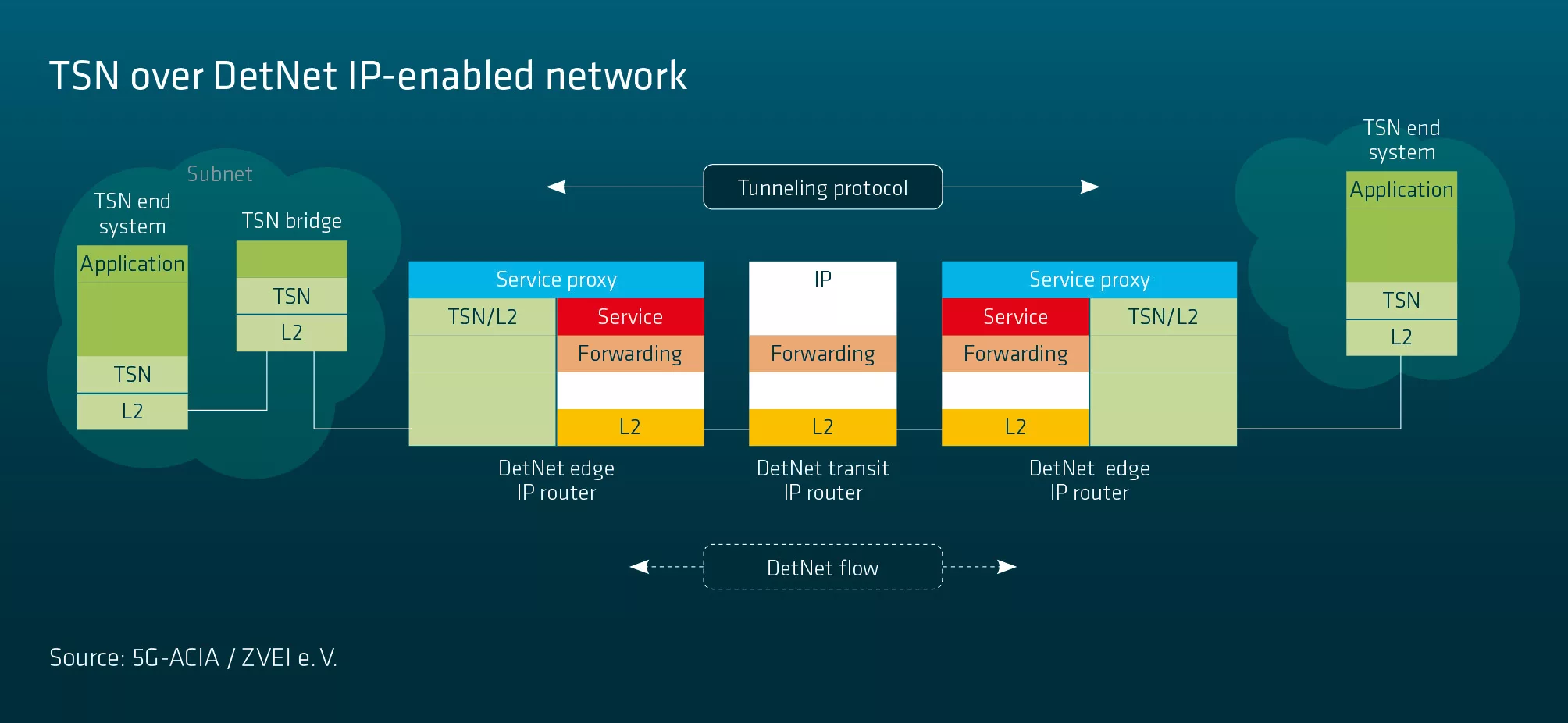
DetNet is useful for interconnecting subnetworks (such as layer 2 TSN segments) while meeting deterministic communication requirements such as low and bounded delays and extremely low packet losses. This makes it easy to scale up the network, something that is challenging to configure in layer 2 networks. In addition, IP-based communication with an IP-based edge or local cloud may be more straightforward to achieve with deterministic communication over layer 3 using DetNet.
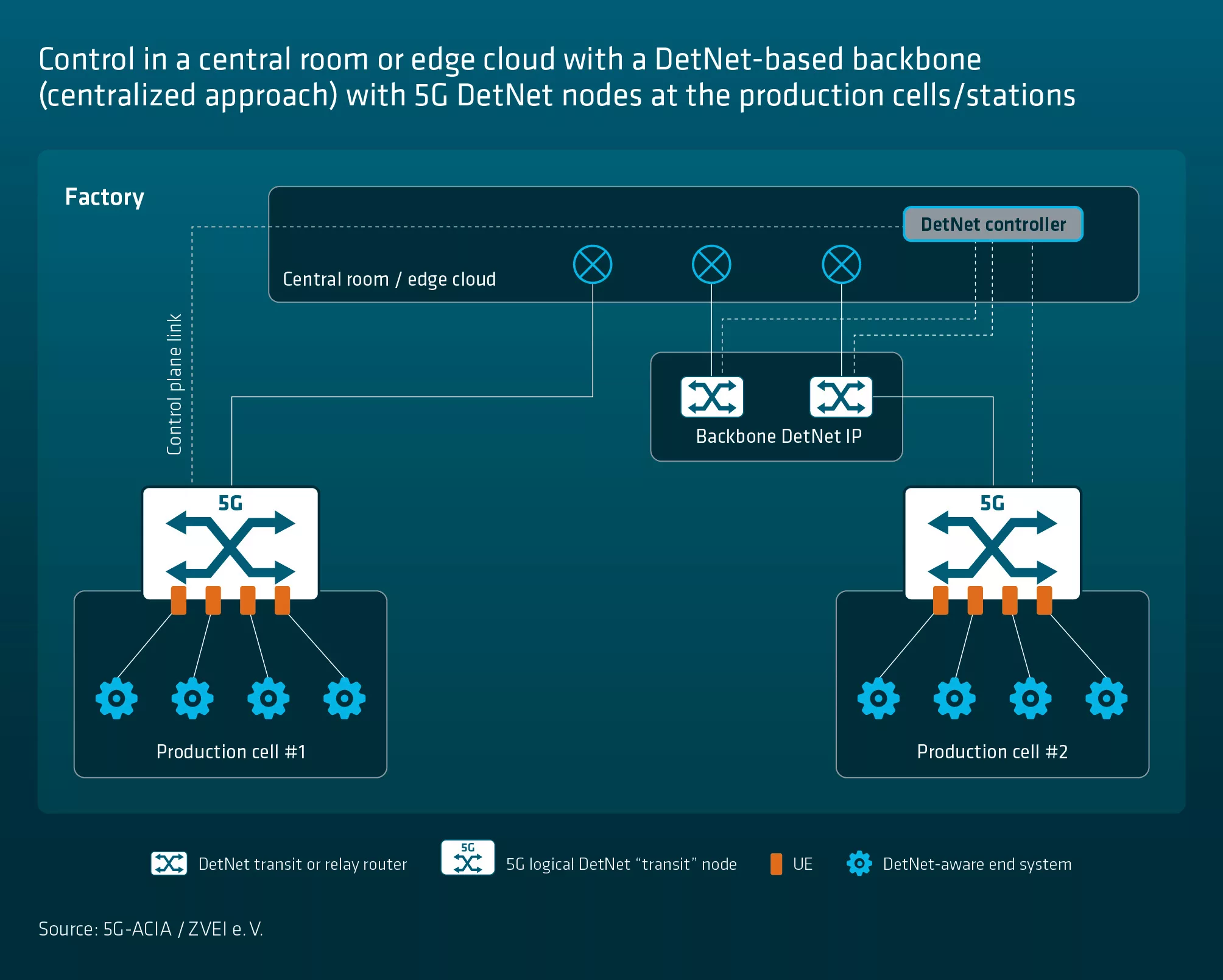
Control may be performed in a central room or in the edge cloud . Depending on the factory’s characteristics, this connectivity can span larger distances. This may be challenging to provide with layer 2 and TSN. The 5G system — acting as a DetNet transit node — directly links machines/production cells to the control room/edge cloud, a DetNet-based backbone, and other machines/production cells.
DetNet is a promising new IP-based technology for deterministic communication as specified by IETF that is potentially applicable to 5G industrial automation use cases. This white paper presents the basic principles and relevant features of the DetNet architecture. Most notably, it provides packet replication elimination and ordering functions (PREOF) and explicit routing. Although DetNet supports MPLS and IP data planes, the focus is on the IP-based DetNet data plane since 5G does not specifically support MPLS. The relationship between DetNet and TSN is also described in terms of their interconnectivity, and their features are compared. DetNet is able to support TSN functions such as scheduled traffic (IEEE 802.1Qbv) and per-stream filtering and policing (IEEE 802.1Qci) [see RFC 9320]. The IETF DetNet WG is collaborating closely with the IEEE 802.1 WG with the aim of supporting a common architecture and similar functionalities. The DetNet controller plane is still being discussed at IETF. With regard to 5G support for DetNet, this white paper surveys the extensions in 3GPP that enable communication with a centralized DetNet controller and how DetNet flows are configured in the 5G system.
Based on analysis of a variety of use cases involving DetNet over 5G, it appears to be a promising option for meeting the requirements of the vast majority of 5G industrial use cases. To illustrate this, 5G deployment scenarios involving DetNet have been presented for two main industrial automation cases, namely pure DetNet deployment and a combination of DetNet and TSN. DetNet offers the additional benefit of interconnecting deterministic traffic flows (DetNet flows) between subnetworks and facilitating connectivity with controllers located in the edge cloud, which is usually IP-based.
Do you want to learn more about this future-oriented topic? Please download or share the 5G-ACIA white paper as a PDF file.
You are currently viewing a placeholder content from YouTube. To access the actual content, click the button below. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.
More InformationYou need to load content from reCAPTCHA to submit the form. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.
More Information