The white paper addresses requirements identified by 5G-ACIA and requirements described in relevant documents of 3GPP Release 17. This white paper identifies requirements outlined in respective 3GPP specifications that are needed to describe and explain operational use cases. However, readers are encouraged to study also other references, e.g. 3GPP TS 22.104 and 22.261, for a complete overview. This white paper focuses on use cases and exposure interface implementation but does not address aspects such as data models and protocols, which are part of interface the actual interface and API specifications.
The requirements for 5G exposure reference points are based on the use cases documented in various 3GPP technical reports and specifications, such as TR 22.804 and on other relevant industry standards and documents. Several relevant use cases and the primary functions to be provided by 5G systems are summarized in the 5G-ACIA, white paper, 5G for Automation in Industry.
They should reflect the following design philosophy:
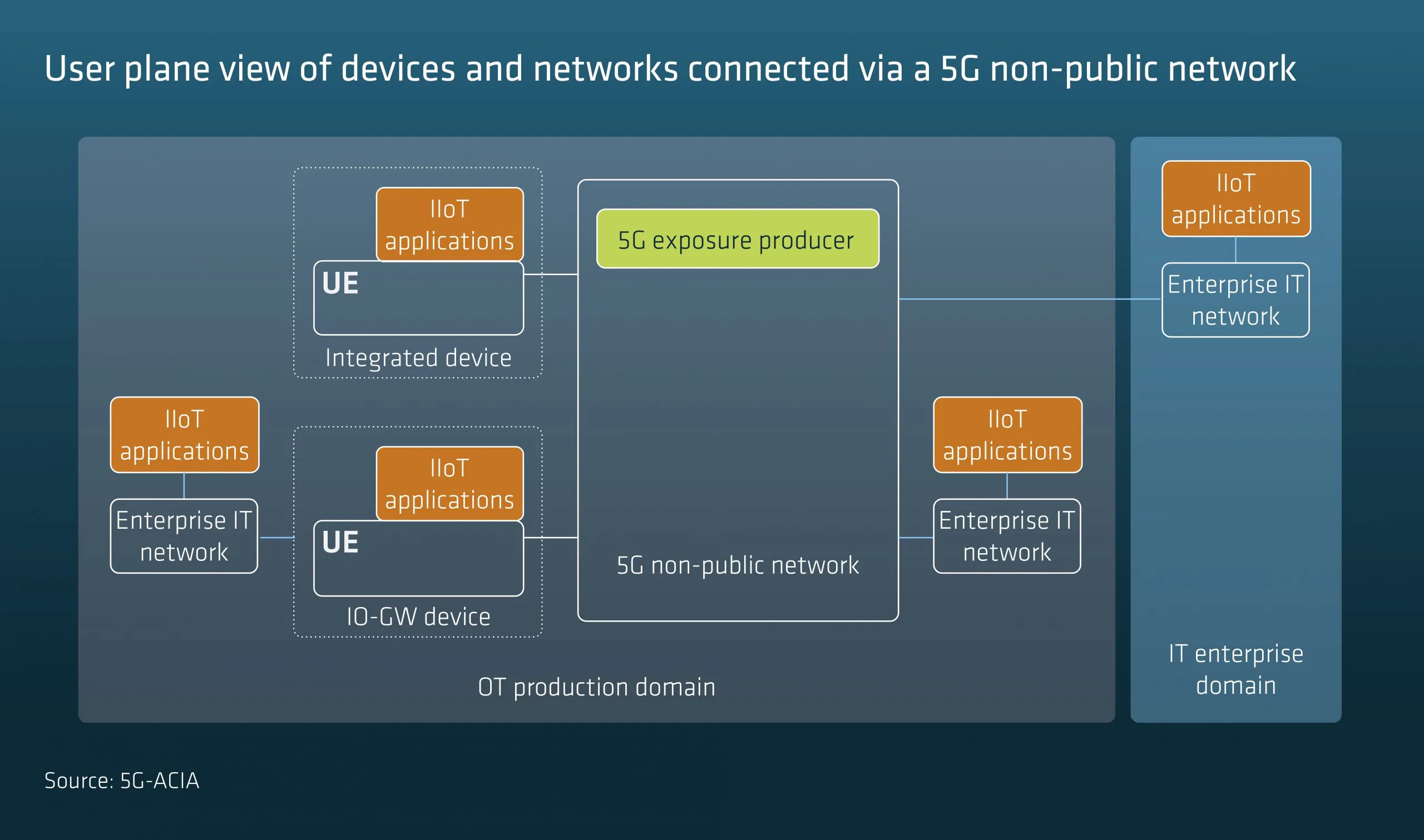
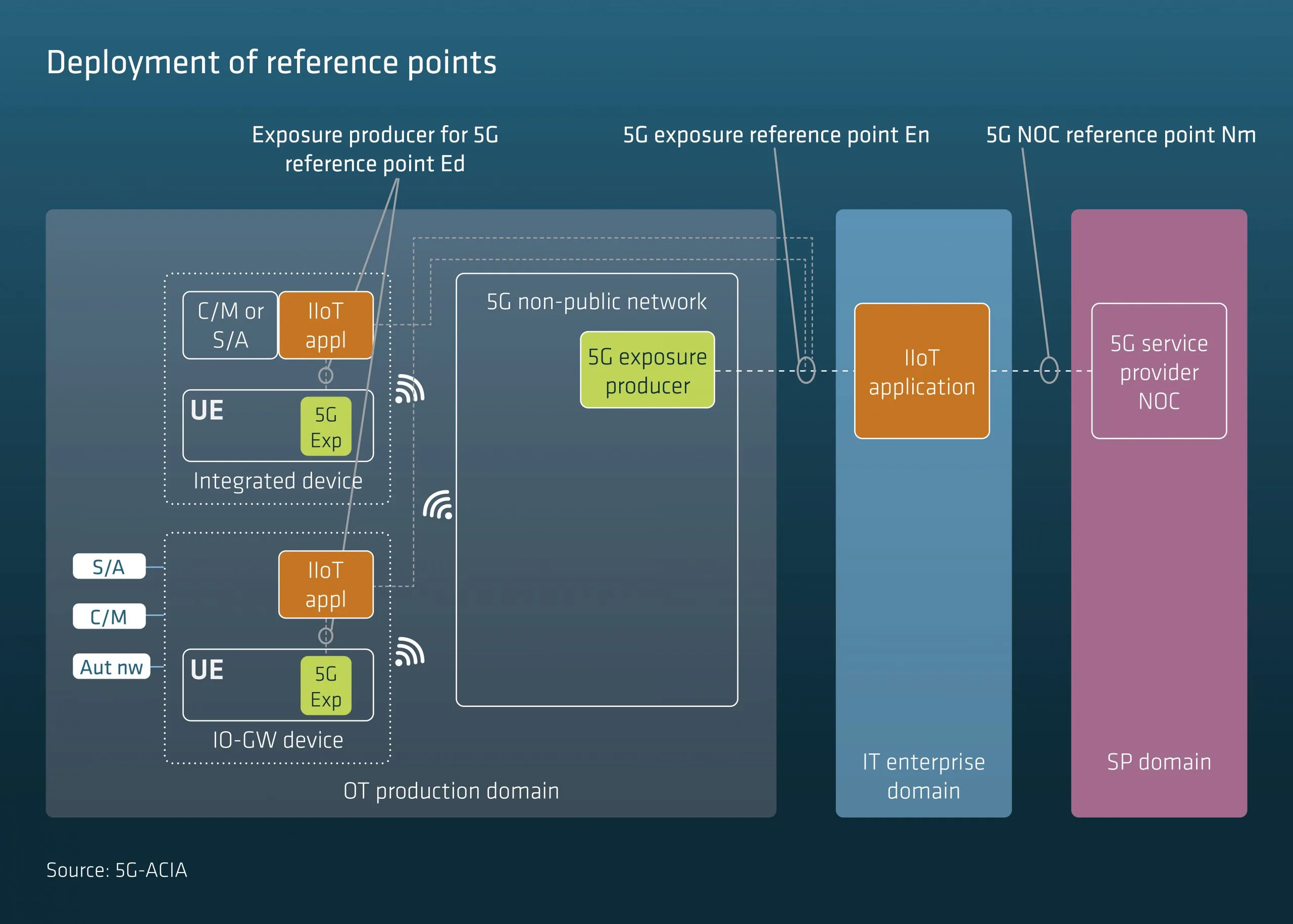
Requirements for 5G exposure reference points are structured into the following categories, device management, network management and security. Some essential solution assumptions are also defined in order to make the specified requirements easier to understand. These assumptions do not preclude any specific exposure interface implementation. One such basic assumption is that the 5G NPN provides communication services between wireless devices, and between wireless devices and wired data networks. The below figure shows how devices can be connected wirelessly to the 5G network. It also depicts non-3GPP operational technology (OT) networks and enterprise IT networks.
This white paper describes the capabilities that a 5G non-public networks must expose towards industrial applications
to enable a range of operational use cases. Those operational use cases are in focus which allow factory operators to perform frequent (daily) tasks without the need to involve the network operator.
To help the reader to better understand how 5G services exposed via the reference points can be consumed by IIoT applications, essential deployment and interconnection solutions are also described.
It should be noted that the capabilities described here can be exposed both by 5G non-public networks deployed in a stand-alone mode
and by networks operated by a mobile network operator on behalf of an enterprise.
Do you want to learn more about this future-oriented topic? Please download or share the 5G-ACIA white paper as a PDF file.